Plastic injection molding is a key manufacturing process for products from medical devices to automotive components and everything in between. Working with an experienced injection molding partner is essential to ensure your product comes out right and stays that way.
Before the heated plastic can be injected, two halves of the mold are securely closed with tremendous force. This clamping pressure can cause quality issues if the machine is not properly sized.
Design for Manufacturability
A key factor in lowering injection molding costs is optimizing the component design for the plastic manufacturing process. This prevents costly redesigns later on that increase both part and mold production costs.
For instance, designers should avoid sharp inside and outside corners, as these concentrate stress at the joint and make it difficult for resin to flow into and out of those regions. Instead, designers should add ample radii that dissipate stress and allow the material to flow freely.
Another cost-saving feature is to minimize the size of bosses, metal threaded inserts and other stressed points of fastening that connect two parts of a case together. Then, designers should use ribs instead to strengthen the base of these features without adding too much mass to the part. Finally, designers should reduce the number of undercuts in the part design. These ledges or cavities interfere with the ejection of parts from injection molds, making them harder and more expensive to manufacture.
Material Selection
Depending on the design requirements of your product, there are thousands of different materials to choose from. The major determining factors are strength, function and cost.
A common choice for injection molding is polyethylene (PE), which is a lightweight yet tough material that can hold up to high impact and chemical resistance. Other common commodity plastics include ABS, polycarbonate, and nylon.
Engineering plastics such as Ultem and Radel offer great stiffness, heat and chemical resistance, and are commonly used in medical and aerospace products. However, it is important to note that engineering polymers are more costly than many other plastics and require additional processing steps.
Another thing to consider is that some resins are hygroscopic, meaning they can absorb water from the air. This can cause voids, discoloration, holes or structural weakness in the final injection molded part, and it is important to have consistent moisture removal during production to avoid this.
Tooling
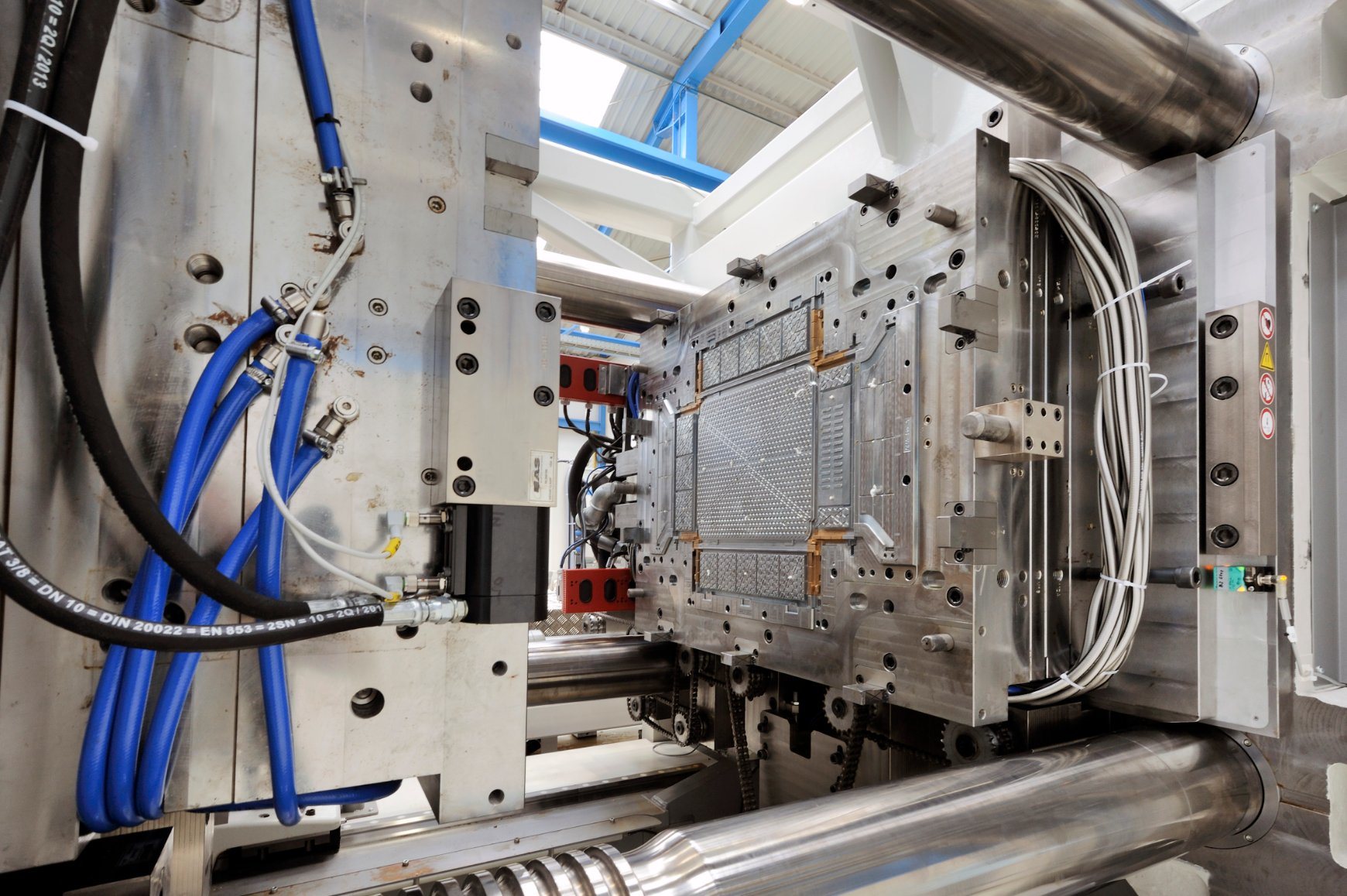
Part art and part science, plastic injection tooling is crucial to guide customers toward an optimized production process, reduced costs, and unparalleled product quality. This step requires significant capital investment and lead time to fabricate a mold capable of making high volume, long-lasting parts. A mold consists of a negative cavity space that receives molten plastic resin to create the finished part. It contains other features such as water lines that aid in cooling and runner systems that provide the mold machine with a flow path for the injected plastic.
Injection molding can be a very cost-effective method of producing complex parts with a high degree of detail. However, the biggest cost drivers are tooling and material costs. The best way to minimize these costs is through careful design, such as adding draft angles to vertical walls to facilitate ejection of the molded part from the mold. This also helps reduce stresses and warping on the wall surface.
Testing
Unlike other manufacturing processes such as CNC machining and 3D printing, plastic injection molding is tailored to mass production of parts at an affordable cost per piece. This makes it an excellent choice for a number of applications including consumer products, automotive and medical devices.
Once a product is designed and the appropriate thermoplastic selected, a toolmaker will produce an injection mold according to specifications provided by the manufacturer. During the injection molding process, two halves of the mold are closed and held under tremendous pressure until most of the plastic has been injected into the tool. This holding time can range from milliseconds to minutes depending on the thermoplastic and part complexity.
Draft angles are a crucial component of the injection molding process as they reduce friction between a cooled, finished plastic part and the mold. Proper draft angles allow for uniform surface finish and reduced wear and tear on the injection mold during production.